The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped our understanding of not only respiratory illnesses but also their far-reaching implications on various body systems, including the kidneys. One area of emerging concern is the connection between COVID-19 and kidney pain. Many individuals recovering from COVID-19 report persistent kidney discomfort, leading to questions about the underlying mechanisms and potential long-term consequences. Understanding kidney pain associated with COVID-19 is crucial for patients seeking relief and comprehensive care. In this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between COVID-19 and kidney pain, offering critical insights and advanced strategies for managing these discomforts effectively.
Analyzing the Link Between COVID-19 and Kidney Pain
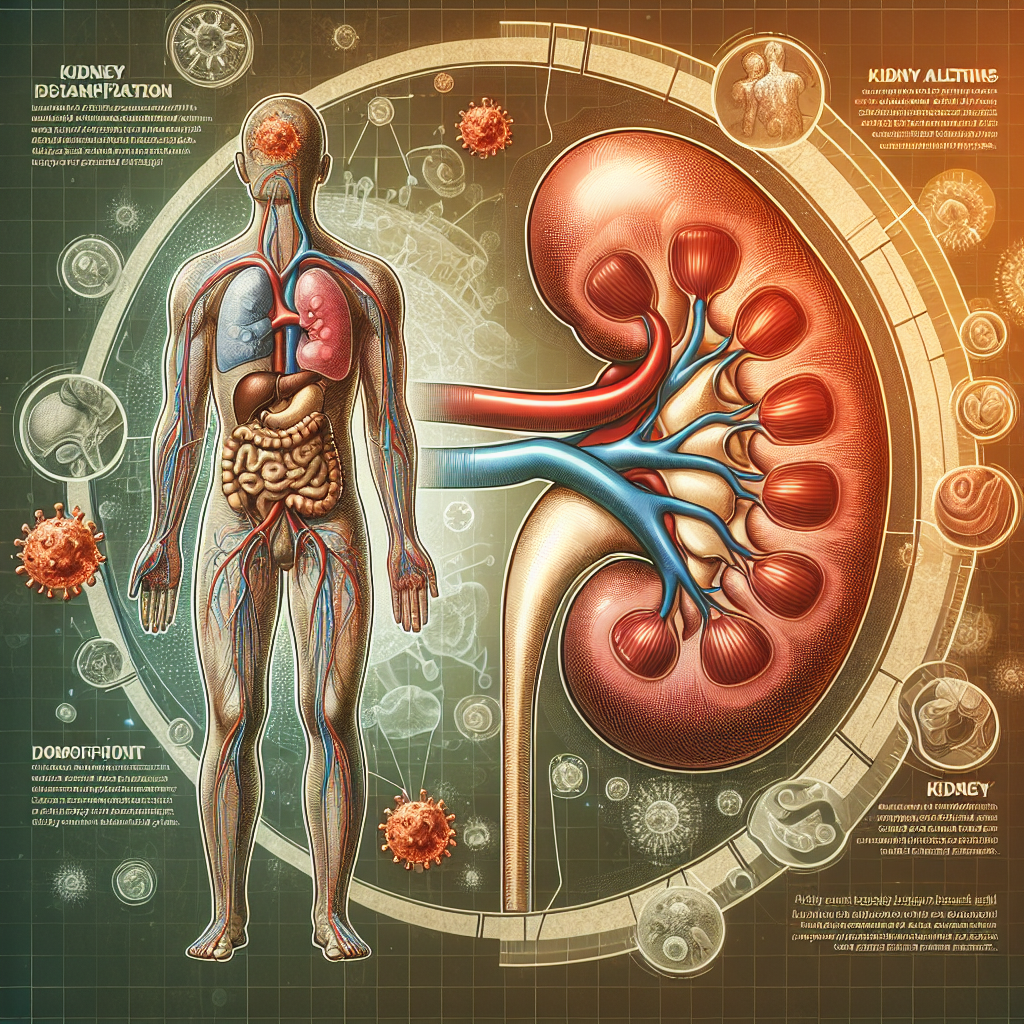
The link between COVID-19 and kidney pain is increasingly recognized in both clinical and research settings. Initial investigations revealed that SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, can infect renal epithelial cells, leading to acute kidney injury (AKI) in some patients. This infection can manifest not only as a reduction in kidney function but also as significant pain or discomfort in the flank area, where the kidneys are located. A growing body of evidence suggests that a subset of COVID-19 patients may experience kidney-related symptoms even after the acute phase of the illness has resolved. This connection raises critical questions about the mechanisms driving kidney pain in post-COVID patients.
Furthermore, the inflammatory response elicited by COVID-19 can contribute to renal complications. Cytokine storms, characterized by excessive immune responses, can lead to systemic inflammation that affects the kidneys. This can result in nephrotoxicity or damage to the renal tissue, presenting as pain or discomfort. Moreover, the complications associated with severe COVID-19, such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and coagulopathy, can further exacerbate kidney discomfort. Patients who experience these symptoms should remain vigilant, as they could indicate underlying kidney issues that require medical attention.
Understanding the nuances of kidney pain associated with COVID-19 is essential for healthcare providers. It is crucial to differentiate between pain stemming from the virus itself and discomfort arising from other non-infectious causes, such as pre-existing renal conditions or medication side effects. Comprehensive assessments, including laboratory evaluations and imaging studies, can help clarify the origins of kidney pain in COVID-19 patients, guiding appropriate management strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Clinical Insights on Managing Kidney Discomfort Post-COVID
Managing kidney discomfort in individuals who have recovered from COVID-19 requires an informed and multifaceted approach. Early recognition of kidney pain and its potential causes is vital for effective intervention. Healthcare professionals should assess the patient’s medical history, including any pre-existing kidney conditions, and conduct thorough evaluations to determine the underlying factors contributing to their discomfort. This may involve blood tests to measure renal function, urinalysis to check for infection or inflammation, and imaging studies to evaluate kidney structure.
Treatment strategies can vary widely based on the identified causes of pain. In cases where inflammation is a significant contributor, anti-inflammatory medications may be beneficial. Additionally, rehydration and electrolyte management are critical, particularly in patients who experienced severe dehydration during their COVID-19 illness. For those with lingering pain, physical therapy may offer relief by improving mobility and reducing muscle tension around the kidneys. Each patient’s care plan should be individualized, reflecting their unique circumstances and health needs.
Beyond pharmacological and physical interventions, educating patients about lifestyle modifications is essential. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and adequate hydration can support kidney health and mitigate discomfort. Patients should also be encouraged to engage in regular, gentle exercise to promote overall wellness. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring of renal function and symptomatology in post-COVID individuals is prudent, as it allows for timely adjustments in management and the potential to prevent more serious complications.
As we navigate the complexities of COVID-19 and its impact on various body systems, understanding kidney pain associated with the virus is paramount for both patients and healthcare providers. By recognizing the mechanisms behind this discomfort and implementing effective management strategies, we can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by long COVID symptoms. If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent kidney pain post-COVID, it’s vital to seek professional medical advice. Understanding your condition and exploring treatment options can empower you on the path to recovery and wellness. Don’t hesitate to reach out for support and guidance, as proactive health management is key to overcoming these challenges.
Understanding Lower Back Pain Linked to COVID-19: Insights and ManagementUnderstanding COVID-19: Navigating Loss of Appetite ChallengesUnderstanding COVID Laryngitis: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentRelevant LinkRelevant LinkRelevant Link